Diabetes Management
Eggplants and Diabetes: A Healthy Addition to Your Diet
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 19 September 2023, Updated on - 26 October 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
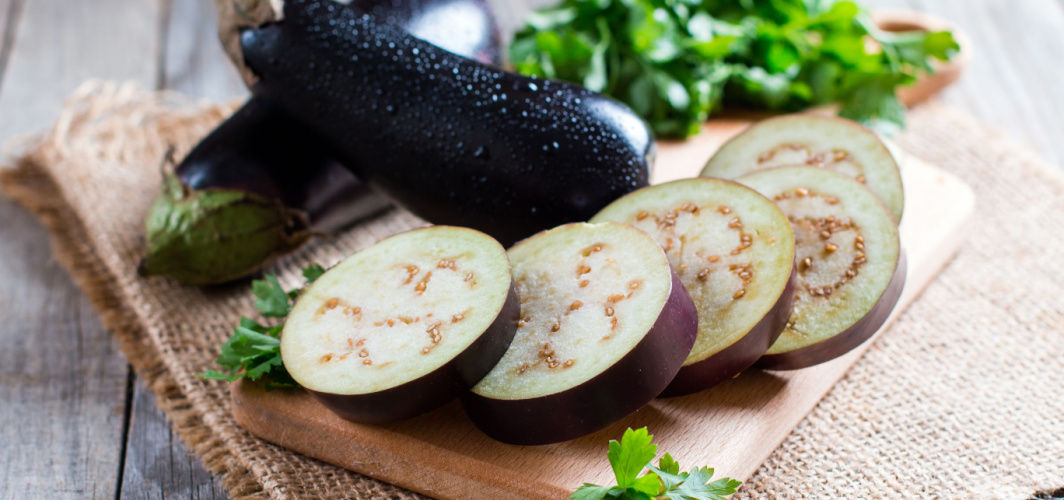

If you have diabetes, you're likely conscious of what you eat to effectively manage your blood sugar levels. Eggplants, also called brinjal or baingan are known for their rich flavour and versatility in cooking, and can be a nutritious addition to a diabetic-friendly diet. In this blog, we'll explore the benefits of including eggplants in your meals and how they can fit into your diabetes management plan.
What is the Nutritional Value of Eggplants?
Eggplants are low in calories and carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for individuals with diabetes. They are a good source of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. 100g raw eggplant contains approximately:
- Calories: 25 Kcal
- Carbohydrates: 6 grams (2% of the Daily Value)
- Dietary Fiber: 3 grams (12% of the Daily Value)
- Protein: 1 gram (2% of the Daily Value)
*The Percent Daily Values are calculated based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Your specific daily values may vary, either being higher or lower, depending on your individual calorie requirements
Benefits for Diabetics
Apart from holding a significant amount of nutritional value, here are other benefits of eggplants for individuals living with diabetes:
- Low in Carbohydrates: Eggplants are relatively low in carbs compared to many other vegetables. This means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels compared to other vegetables.
- Rich in Fiber: The fiber content in eggplants can aid in regulating blood sugar. Dietary fiber slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, helping to prevent spikes in blood sugar after meals.
- Antioxidant Properties: Eggplants contain antioxidants, including vitamins C and K, which can help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress.
- Heart Health: Maintaining cardiovascular health is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Eggplants are a source of potassium, when consumed in moderation it helps regulate blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart complications often associated with diabetes.
- Weight Management: Due to their low-calorie content and ability to make you feel full, eggplants can be a valuable addition to a weight management strategy, which is often a key aspect of diabetes management.
How to Incorporate Eggplants into Your Diet?
To enjoy the benefits of eggplants while managing diabetes:
- Include grilled or roasted eggplant in salads.
- Make a hearty eggplant stew or curry with plenty of fiber-rich vegetables.
- Experiment with stuffed eggplants filled with lean protein and vegetables.
Conclusion
Remember that portion control is essential, as overconsumption of any food, even low-carb vegetables like eggplants, can impact blood sugar levels. It's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to tailor your diet to your specific diabetes management needs.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Is Increased Thirst A Sign Of Diabetes?
Excessive thirst can be a warning sign of diabetes. Learn about how you can manage and prevent this condition.

Diabetes Management
Diabetes & Sleep Cycle: Is there a Connection?
Diabetes can interfere with your sleep cycle as it causes fluctuating blood sugar levels. This chronic condition affects millions worldwide. It can trigger insomnia, night sweats, and even nightmares since high and low blood sugar extremes disturb the sleep cycle. Moreover, diabetes elevates the risk of sleep apnea, characterised by pauses in breathing during sleep. Neuropathy, a frequent complication of diabetes, can also lead to discomfort in the legs and feet. Recognizing these connections and being proactive in diabetes management can improve sleep quality and overall well-being.
Diabetes Management
Diabetic Foot: Can it be Prevented?
The development of diabetic foot can be prevented through various measures. Effective prevention includes regular foot care, such as daily inspection and cleaning, wearing comfortable and proper-fitting shoes, managing blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, and seeking immediate medical attention for any foot issues.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Is Increased Thirst A Sign Of Diabetes?
Excessive thirst can be a warning sign of diabetes. Learn about how you can manage and prevent this condition.

Diabetes Management
Diabetes & Sleep Cycle: Is there a Connection?
Diabetes can interfere with your sleep cycle as it causes fluctuating blood sugar levels. This chronic condition affects millions worldwide. It can trigger insomnia, night sweats, and even nightmares since high and low blood sugar extremes disturb the sleep cycle. Moreover, diabetes elevates the risk of sleep apnea, characterised by pauses in breathing during sleep. Neuropathy, a frequent complication of diabetes, can also lead to discomfort in the legs and feet. Recognizing these connections and being proactive in diabetes management can improve sleep quality and overall well-being.

Diabetes Management
Diabetic Foot: Can it be Prevented?
The development of diabetic foot can be prevented through various measures. Effective prevention includes regular foot care, such as daily inspection and cleaning, wearing comfortable and proper-fitting shoes, managing blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, and seeking immediate medical attention for any foot issues.
