Diabetes Management
Are You at Risk for Diabetes? This Simple Test Can Tell
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 27 May 2022, Updated on - 06 September 2023
Share this article
0
66 likes

Glucose build-up in the blood can be extremely harmful as it can damage the vessels that supply blood to vital organs, thereby increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve problems. Physicians often recommend an HbA1c test to assess their role in the early diagnosis of diabetes. The article explains the important aspects of this key test in detail below.
What is the HbA1C test?
A haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It is different from a glucometer or finger-prick test that tells your current blood glucose levels. Higher HbA1c levels mean you have too much glucose (sugar) in your blood, which can increase the risk of health complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
How Does it Work?
The HbA1c test works by measuring the average amount of glycated haemoglobin in your bloodstream over the past three months. Glycated haemoglobin is formed when the excess glucose in your blood attaches itself to the haemoglobin (oxygen-carrying proteins found in red blood cells). Since the red blood cells have a lifespan of only 3 months, the test reveals average values for that duration only. However, if your glucose levels have been elevated over recent weeks, your HbA1c test results will be higher.
Who Needs It?
The HbA1c test is generally used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. It is also used by diabetics to check if their blood glucose levels are under control. A baseline HbA1c test is usually recommended for every adult aged 45 years and above. However, it can also be prescribed to those aged below 45 years if they have one or more of the following risk factors:
- Are overweight
- Have hypertension
- Have cardiovascular disease
- Are physically inactive
The frequency of HbA1c tests for those who have already been diagnosed with diabetes depends on certain factors such as:
- Type of diabetes (type 1 or 2)
- Blood glucose levels
- Existing treatment plan
How To Prepare For A HbA1C Test?
Unlike a glucometer or finger-prick test, you don’t have to fast overnight before the test. The test doesn’t require any special preparation. However, if the test is being conducted alongside other diagnostic tests, then you may have to prepare for those tests. Ask your physician to know more.
Interpreting Test Results
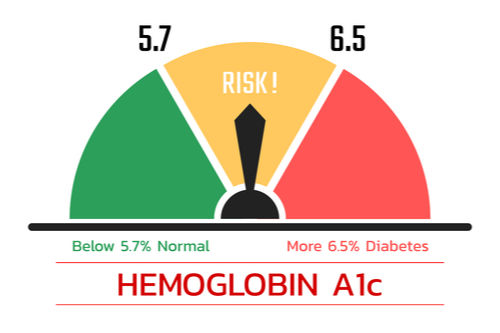
The normal ranges of haemoglobin A1c levels are:
- Normal: not more than 5.7%
- Prediabetes: between 5.7% and 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
Factors That May Affect HbA1C Test Results
Certain medical conditions can cause deviation in your HbA1c test results. Some of these conditions are:
- Severe anaemia
- Liver disease
- Kidney failure
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Thalassemia
- Blood loss or blood transfusions
- Pregnancy

Other factors that may impact your test results are high cholesterol levels and the use of vitamin C and E supplements.
HbA1c test is a key diagnostic test that is mostly used to diagnose and monitor diabetes in a person. The test works by measuring the amount of glucose attached to the haemoglobin protein in red blood cells. Unlike the finger prick test, the HbA1c test can help reveal your average blood glucose levels for the last 3 months. Conditions like anaemia, kidney failure, and liver disease can impact the results. Therefore, it is recommended to share the test report with a physician who may prescribe additional tests to get a better picture.
You can also manage your diabetes like a pro with Apollo 24|7's 12-week empower programme.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
6 Tips To Prepare For Diabetes Test
Diabetes is a chronic condition that needs to be diagnosed early to prevent complications. Diagnostic tests quickly detect high blood sugar levels. Though painless and quick, preparation can take hours due to fasting overnight. This article will guide you on how to prepare for the test.

Diabetes Management
Keeping an Eye on Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication arising from uncontrolled blood sugar levels. The increased blood glucose levels damage the blood vessels in the retina. It progresses through stages: background retinopathy (micro-aneurysms), and proliferative retinopathy (abnormal blood vessel growth and vision loss). Regular screenings and lifestyle modifications can help prevent or manage diabetic retinopathy.

Diabetes Management
Can Coffee Reduce The Severity Of Liver Disease In People With Type 2 Diabetes?
There is emerging evidence suggesting that coffee consumption may reduce the severity of liver disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Coffee's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as its potential to lower liver enzyme levels, are believed to contribute to these effects. However, further research is needed to establish the precise mechanisms and optimal coffee consumption guidelines for liver health in this population.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
6 Tips To Prepare For Diabetes Test
Diabetes is a chronic condition that needs to be diagnosed early to prevent complications. Diagnostic tests quickly detect high blood sugar levels. Though painless and quick, preparation can take hours due to fasting overnight. This article will guide you on how to prepare for the test.

Diabetes Management
Keeping an Eye on Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication arising from uncontrolled blood sugar levels. The increased blood glucose levels damage the blood vessels in the retina. It progresses through stages: background retinopathy (micro-aneurysms), and proliferative retinopathy (abnormal blood vessel growth and vision loss). Regular screenings and lifestyle modifications can help prevent or manage diabetic retinopathy.

Diabetes Management
Can Coffee Reduce The Severity Of Liver Disease In People With Type 2 Diabetes?
There is emerging evidence suggesting that coffee consumption may reduce the severity of liver disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Coffee's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as its potential to lower liver enzyme levels, are believed to contribute to these effects. However, further research is needed to establish the precise mechanisms and optimal coffee consumption guidelines for liver health in this population.