Diabetes Management
Diabetic Neuropathy: Why the Burning Sensation in Your Feet Should Not be Ignored?
3 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 05 December 2020, Updated on - 27 August 2023
Share this article
1
9 likes

What is diabetic neuropathy?
- Sensory neuropathy: Damage to the nerves that detect touch and temperature - commonly affects the feet and hands.
- Motor neuropathy: Damage to the nerves that help in muscle movement.
- Autonomic neuropathy: Damage to the nerves that control involuntary actions of the body such as digestion.
What are the signs of diabetic neuropathy?
- Numbness, especially in the extremities, i.e., toes, fingers
- Tingling sensation
- Pain in the body
- Weakness in the limbs
- Difficulties with walking, balance, and coordination
- Loss of muscle mass in the feet, legs, hands, and hips
Who is more likely to get diabetic neuropathy?
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Weight issues
- High blood pressure
- Age above 40 years
- High levels of triglycerides
- Habits such as smoking and consuming alcohol
- Chronic liver or kidney disease
- Vitamin B deficiency
- Prolonged diabetes (living with diabetes for a long period of time)
- Other diseases and anti-cancer drugs
- Coronary heart disease or other heart condition.
Can diabetic neuropathy be prevented?
- Adhere to the medications prescribed by the doctor
- Follow healthy eating habits and consume whole, nutritious food
- Limit the consumption of high-fat and high-calorie processed foods
- Reduce salt consumption to keep blood pressure in the normal range
- Take up some form of moderate-intensity exercise such as brisk walking, riding a bicycle or swimming to stay physically active
- Quit smoking to reduce the risk of neuropathy
- Significantly reduce the consumption of alcohol.
- Examine the feet every day for any red spots, cuts, swellings or blisters
- Nails of the feet should be cut and trimmed carefully
- Pat dry the feet after bathing and moisturize them later
- Wear well-fitted shoes and wear thick, soft, seamless socks along with them.
Takeaway
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Neurologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
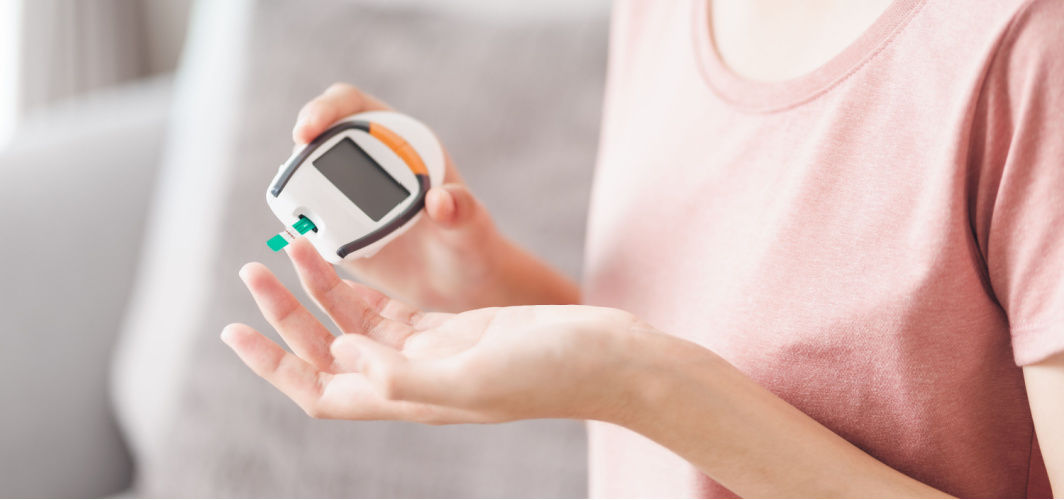
3 Common Mistakes to Avoid While Blood Sugar Testing
Effective diabetes management relies on precise blood sugar testing and lifestyle adjustments. These include not pricking the same finger daily, maintaining proper hand hygiene, and timing tests correctly (preferably before eating or waiting two hours after a meal). Accurate testing empowers individuals to collaborate effectively with their healthcare teams, make informed decisions about diet, medication, and lifestyle, and ultimately take better control of their condition for a stress-free and healthier life.

Diabetes Management
Eating Out in Festivals: Tips for a Healthier Dining Experience
Dining out with diabetes can still be a delightful experience with some careful choices. To enjoy restaurant meals while managing your blood sugar levels, plan ahead by reviewing the menu and choosing dishes wisely, focusing on lean proteins and vegetables. Watch portion sizes and control carbohydrates. Request dressings and sauces on the side and opt for healthier beverage choices. Be mindful of desserts and share them if needed. Communicate your dietary needs with the person who is serving, and try to stick to your regular meal schedule for stable blood sugar levels. Dining out can be a pleasure with these strategies in mind.
Diabetes Management
Prevention Tips For Diabetes Foot Infection
In case of uncontrolled diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves, resulting in poor blood circulation. This can increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections. The reduced blood flow and loss of sensation in the feet can make it difficult to detect injuries or infections, leading to delayed healing and potential complications.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
3 Common Mistakes to Avoid While Blood Sugar Testing
Effective diabetes management relies on precise blood sugar testing and lifestyle adjustments. These include not pricking the same finger daily, maintaining proper hand hygiene, and timing tests correctly (preferably before eating or waiting two hours after a meal). Accurate testing empowers individuals to collaborate effectively with their healthcare teams, make informed decisions about diet, medication, and lifestyle, and ultimately take better control of their condition for a stress-free and healthier life.

Diabetes Management
Eating Out in Festivals: Tips for a Healthier Dining Experience
Dining out with diabetes can still be a delightful experience with some careful choices. To enjoy restaurant meals while managing your blood sugar levels, plan ahead by reviewing the menu and choosing dishes wisely, focusing on lean proteins and vegetables. Watch portion sizes and control carbohydrates. Request dressings and sauces on the side and opt for healthier beverage choices. Be mindful of desserts and share them if needed. Communicate your dietary needs with the person who is serving, and try to stick to your regular meal schedule for stable blood sugar levels. Dining out can be a pleasure with these strategies in mind.

Diabetes Management
Prevention Tips For Diabetes Foot Infection
In case of uncontrolled diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves, resulting in poor blood circulation. This can increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections. The reduced blood flow and loss of sensation in the feet can make it difficult to detect injuries or infections, leading to delayed healing and potential complications.
