Diabetes Management
How to Check Sugar Levels After a Meal?
2 min read

Managing blood sugar levels is an important aspect of diabetes care, and monitoring your sugar levels after meals can provide valuable insights into how different foods and portions affect your body. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to check sugar levels after a meal to help you maintain better control of your diabetes.
1. Use a Glucometer
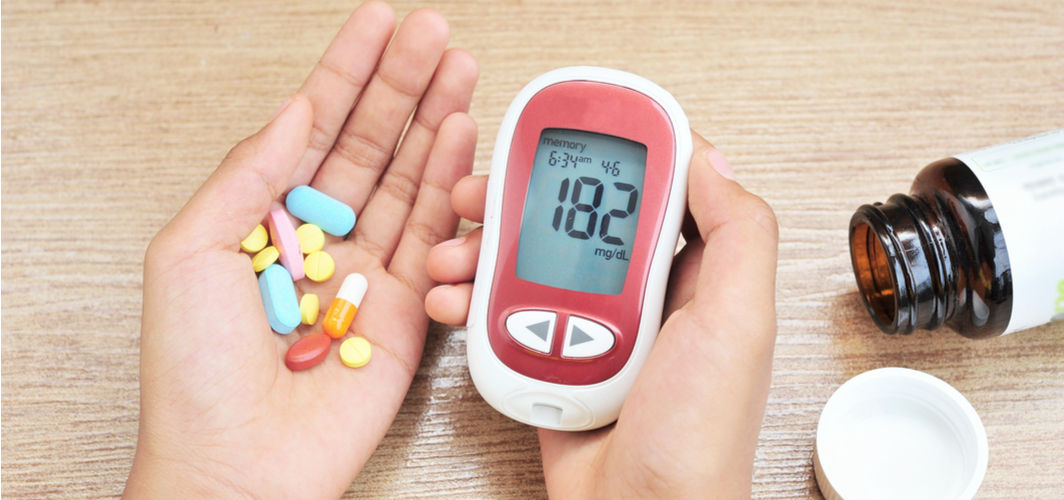
The primary tool for checking post-meal sugar levels is a glucometer, a small and portable device that measures blood glucose levels. Before you start, ensure that the pricking area is clean and the device is properly calibrated according to the manufacturer's instructions.
2. Timing Matters
To get an accurate reading, it's essential to check your sugar levels at the right time. Typically, it's recommended to test 1 to 2 hours after your meal. This timing allows you to see how your body processes the carbohydrates from your meal.
3. Hand Hygiene
Before testing, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Residues from food or other substances on your fingers can contaminate the test strip, leading to inaccurate results.
4. Prepare the Lancet Device
Most glucometers use a lancet device to prick your fingertip for a blood sample. Follow the instructions provided with your device to prepare and use the lancet.
5. Obtain a Blood Sample
Place a test strip into the glucometer and use the lancet device to prick the side of your fingertip. Gently squeeze your fingertip to collect a small drop of blood and apply it to the test strip.
6. Wait for the Reading
The glucometer will analyse the blood sample and provide a numerical reading of your sugar level on its display screen.
7. Record Your Results
Make it a habit to keep a record of your post-meal sugar levels. This tracking helps you and your healthcare provider identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
8. Interpret the Results:
Understanding your post-meal sugar levels is crucial. In general, the normal post-meal blood sugar level for individuals with diabetes is under 180 mg/dL.
9. Take Action:
Based on your post-meal sugar levels, you and your healthcare provider can decide if any changes are needed in your diet, medication, or exercise routine.
10. Seek Guidance:
Always consult with a diabetologist for guidance on monitoring and interpreting your post-meal sugar levels. They can provide personalised advice and help you create a comprehensive diabetes management plan.
Conclusion
Checking sugar levels after a meal empowers individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their dietary choices and medication. It's a valuable tool for achieving better blood sugar control and ultimately improving overall health and well-being.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Log. Track. Learn- Here’s How You Can Simplify Your Diabetes Management
Simplify your diabetes management with Apollo 24|7's diabetes self-management tool. Track your glucose levels, monitor physical activity, sync glucometers, understand the impact of your meals on your sugar levels and stay informed through Health Bites. You can try this user-friendly tool that empowers you to make informed decisions, achieve better blood sugar control, and lead a healthier life while simplifying your diabetes management journey.
Diabetes Management
Blood Pressure Lowering Medicines May Reduce the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Blood pressure-lowering medicines may reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some medications, such as ACE inhibitors and ARBs, have shown potential in improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. By controlling blood pressure levels, these medications may help mitigate the risk and progression of type 2 diabetes in individuals with hypertension.

Diabetes Management
The Best Time to Exercise in Diabetes
Exercise plays a crucial role in diabetes management, benefiting both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes individuals. The timing of exercise matters as well. For Type 2 diabetes, morning workouts should be preceded by a small meal to prevent blood glucose spikes. Conversely, people with Type 1 diabetes are advised to exercise in the morning to avoid later-day hypoglycemia. High-intensity interval training post-lunch suits Type 2 diabetes, while late evening exercise can affect people with Type 1 diabetes, mitigated with insulin adjustments. Consulting healthcare professionals for a personalised exercise plan is crucial for effective diabetes management.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
Log. Track. Learn- Here’s How You Can Simplify Your Diabetes Management
Simplify your diabetes management with Apollo 24|7's diabetes self-management tool. Track your glucose levels, monitor physical activity, sync glucometers, understand the impact of your meals on your sugar levels and stay informed through Health Bites. You can try this user-friendly tool that empowers you to make informed decisions, achieve better blood sugar control, and lead a healthier life while simplifying your diabetes management journey.

Diabetes Management
Blood Pressure Lowering Medicines May Reduce the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Blood pressure-lowering medicines may reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Some medications, such as ACE inhibitors and ARBs, have shown potential in improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. By controlling blood pressure levels, these medications may help mitigate the risk and progression of type 2 diabetes in individuals with hypertension.

Diabetes Management
The Best Time to Exercise in Diabetes
Exercise plays a crucial role in diabetes management, benefiting both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes individuals. The timing of exercise matters as well. For Type 2 diabetes, morning workouts should be preceded by a small meal to prevent blood glucose spikes. Conversely, people with Type 1 diabetes are advised to exercise in the morning to avoid later-day hypoglycemia. High-intensity interval training post-lunch suits Type 2 diabetes, while late evening exercise can affect people with Type 1 diabetes, mitigated with insulin adjustments. Consulting healthcare professionals for a personalised exercise plan is crucial for effective diabetes management.
