Diabetes Management
Hypoglycaemia: Know What Happens When Your Blood Sugar Drops!
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 20 January 2023, Updated on - 01 June 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
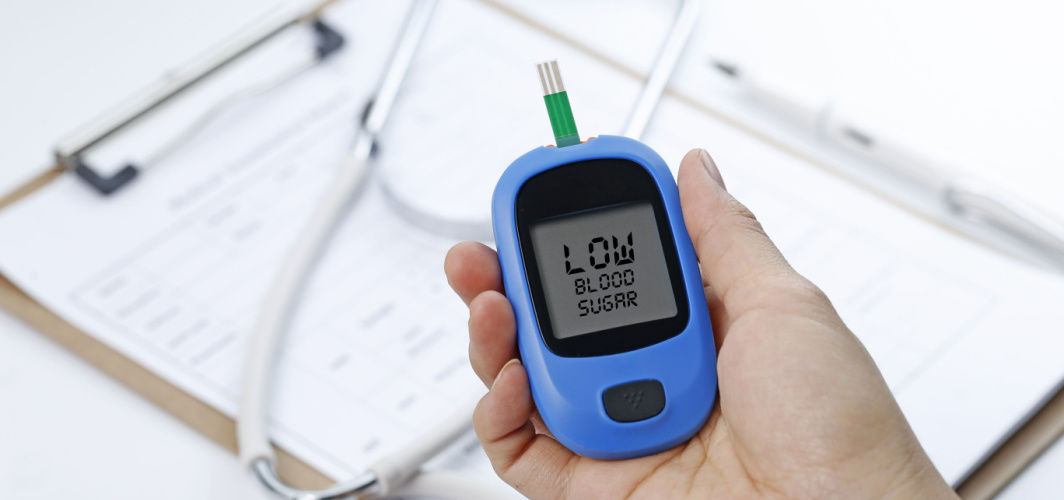

Have you ever experienced a sudden drop in your energy levels leaving you all weak and shaky? It can be hypoglycaemia. Hypoglycaemia is a medical condition characterized by lower-than-normal blood sugar levels. While it is more common in diabetics, it can happen in healthy people too. When a person with diabetes mellitus lacks sufficient glucose in their blood, they develop diabetic hypoglycaemia. However, in non-diabetics hypoglycemia can occur due to some underlying medical conditions or food habits. Let us know more about the condition and how to recognise it.
What is the blood sugar level in hypoglycaemia?
A fasting blood sugar level (in the morning before eating anything) of 99 mg/dL or less is considered normal. However, blood sugar levels of less than 70 mg/dl would be considered hypoglycaemia.
How do you know if you have low blood sugar?
Symptoms of hypoglycaemia can range from short-term effects like disorientation and light-headedness to more severe ones like convulsions, coma, and even death, in extreme cases. Some typical symptoms that you may face include:
- Hunger
- Shakiness and sweating
- Anxiety or irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Light-headedness
- Vision problems
- Slurred speech
- Clumsiness
- Sleep disturbances
It must be noted that severe hypoglycaemia can result in seizures and loss of consciousness. Therefore, people must consult a doctor if they experience any of the signs mentioned above.
Why is my blood sugar level low?
The causes of hypoglycaemia can be different in diabetics and non-diabetics. Diabetics can have low blood sugar levels due to:
- Not eating enough carbs to metabolise the amount of insulin taken
- Skipping meals
- Consuming alcohol
- Taking too much insulin
- Increased physical activity without changing your diet or diabetes medication
For non-diabetic people, the causes of hypoglycaemia can be:
- Intake of antibiotics and medicines for malaria and pneumonia
- Hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone levels)
- A side effect of weight loss surgeries
- Liver or kidney problems
- Excessive alcohol consumption
What is the treatment for hypoglycaemia?
Hypoglycaemia should be treated immediately to prevent severe complications. One must start with the 15-15 rule, which includes:
- Eat or drink 15 grams of something sweet, like dextrose tablets or fruit juice, to raise your blood sugar.
- Check your blood sugar after 15 minutes, and if it's still low, eat something sweet again.
Severe hypoglycaemia can lead to loss of consciousness. This is an emergency situation that would require immediate medical intervention. Do not try to feed an unconscious person as it could cause them to choke.
FAQs:
1. What is a common test for hypoglycaemia?
Your doctor will check your blood sugar levels at various times of the day to notice any pattern. A blood test would be recommended to check your insulin levels and rule out other conditions that may cause hypoglycaemia.
2. Is there a special diet I should follow for hypoglycaemia?
It is advised to consume small meals every 3 to 4 hours throughout the day. Consuming vegetables, non-meat protein, nuts, dairy, and whole grains will assist in keeping blood sugar levels within the limits.
3. Can stress cause hypoglycaemia?
Sometimes, long-term stress may cause changes in blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of hypoglycaemia.
4. Can hypoglycaemia occur without diabetes?
Yes, hypoglycaemia can be seen in healthy individuals too.
5. What food to avoid if I have hypoglycaemia?
You should not consume foods with high fibre or high fat as they slow down the rate at which sugar is absorbed by the body.
Hypoglycaemia when left untreated, can cause long-term damage. If you experience a drop in your sugar levels too often, don't wait to consult a diabetologist to determine the underlying reason.
Talk To An Apollo Diabetologist
You can also manage your diabetes like a pro with Apollo 24|7's 12-week empower programme.
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
Diabetes Management
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
Getting A Blood Sugar Test Done? Know How To Read The Report!
One of the most important aspects of managing diabetes is the constant monitoring of your blood sugar levels. This can be done through blood sugar tests. This blog covers what different types of blood sugar tests are and how to read their reports.

Diabetes Management
Eating Out in Festivals: Tips for a Healthier Dining Experience
Dining out with diabetes can still be a delightful experience with some careful choices. To enjoy restaurant meals while managing your blood sugar levels, plan ahead by reviewing the menu and choosing dishes wisely, focusing on lean proteins and vegetables. Watch portion sizes and control carbohydrates. Request dressings and sauces on the side and opt for healthier beverage choices. Be mindful of desserts and share them if needed. Communicate your dietary needs with the person who is serving, and try to stick to your regular meal schedule for stable blood sugar levels. Dining out can be a pleasure with these strategies in mind.

Diabetes Management
Vision Troubles in Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment
While diabetes raises the chances of several eye-related complications, it can easily be managed with early diagnosis and proper treatment. Regular eye exams are vital for the early detection of conditions like macular edema, diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Diagnosis involves retinal imaging, comprehensive exams, visual acuity testing to measure the ability of the eye to differentiate shapes and details of objects at a given distance, and tonometry to measure intraocular pressure. Treatment options include blood sugar control, medications, laser therapy, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Getting A Blood Sugar Test Done? Know How To Read The Report!
One of the most important aspects of managing diabetes is the constant monitoring of your blood sugar levels. This can be done through blood sugar tests. This blog covers what different types of blood sugar tests are and how to read their reports.

Diabetes Management
Eating Out in Festivals: Tips for a Healthier Dining Experience
Dining out with diabetes can still be a delightful experience with some careful choices. To enjoy restaurant meals while managing your blood sugar levels, plan ahead by reviewing the menu and choosing dishes wisely, focusing on lean proteins and vegetables. Watch portion sizes and control carbohydrates. Request dressings and sauces on the side and opt for healthier beverage choices. Be mindful of desserts and share them if needed. Communicate your dietary needs with the person who is serving, and try to stick to your regular meal schedule for stable blood sugar levels. Dining out can be a pleasure with these strategies in mind.

Diabetes Management
Vision Troubles in Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment
While diabetes raises the chances of several eye-related complications, it can easily be managed with early diagnosis and proper treatment. Regular eye exams are vital for the early detection of conditions like macular edema, diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Diagnosis involves retinal imaging, comprehensive exams, visual acuity testing to measure the ability of the eye to differentiate shapes and details of objects at a given distance, and tonometry to measure intraocular pressure. Treatment options include blood sugar control, medications, laser therapy, surgery, and lifestyle changes.