Diabetes Management
What Not to Eat in Diabetes: A Guide to Managing Your Diet
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 29 September 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
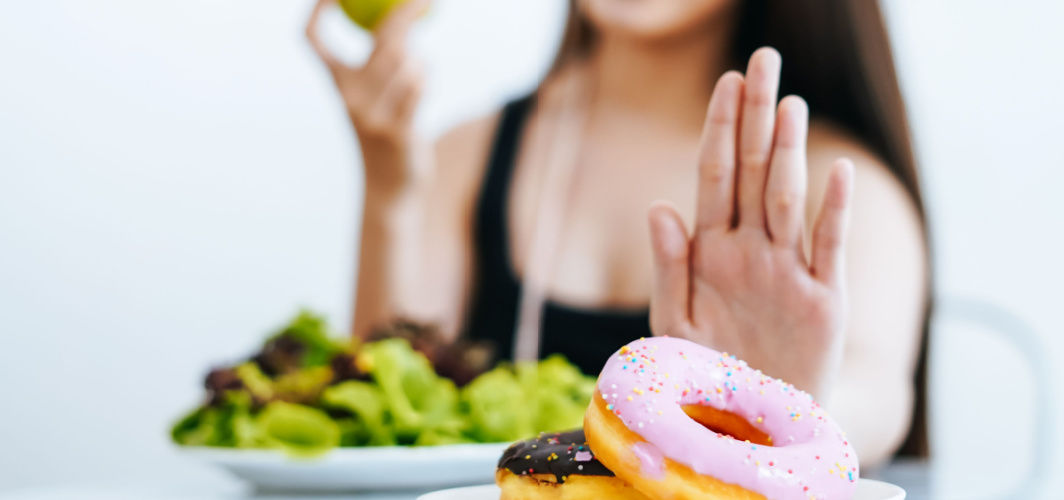

For individuals living with diabetes, dietary choices play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and overall health. Understanding what foods to avoid is as important as knowing what to include in your diet. In this article, we'll explore what not to eat in diabetes to help you make informed and healthier choices.
1. Sugary Beverages
One of the top things to avoid in diabetes is sugary beverages like soda, specially packaged fruit juices, and energy drinks. These drinks are loaded with high amounts of sugar, which can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Opt for water, herbal tea, or unsweetened natural beverages instead.
2. Sugary Snacks and Sweets
Candies, cookies, cakes, and other sugary snacks can impact blood sugar levels. These items are often high in refined carbohydrates and offer little nutritional value. Choose healthier snacks like a combination of nuts, seeds, or low-fat yoghurt sprinkled with pomegranate or diced apple.
3. White Bread and Refined Grains
White bread or white Indian bread commonly known as ‘naan’, white rice, and most processed cereals are examples of refined grains that can cause sharp increases in blood sugar. Instead, opt for whole grains like whole wheat bread, brown rice, jowar, bajra, quinoa, and oats, which have a lower glycemic index.
4. Fried and Fatty Foods
Fried foods like pakoras, bhajias, french fries and fried chicken are typically high in unhealthy trans fats and saturated fats. These fats can contribute to insulin resistance and increase the risk of heart disease. Choose cooking methods like baking, grilling, or steaming.
5. Full-Fat Dairy
Full-fat dairy products (milk, cheese, yoghurt, etc.) contain saturated fats that can negatively impact insulin sensitivity. Opt for low-fat or non-fat dairy options or consider plant-based alternatives like almond or soy milk.
6. Processed Meats
Processed meats like cutlet mix, salami, bacon, sausages, and hot dogs often contain added sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats. These should be replaced with lean protein sources like skinless poultry, fish, eggs, tofu, or legumes.
7. Sweetened Condiments
Condiments like ketchup, barbecue sauce, and salad dressings can hide significant amounts of added sugar. Check labels for sugar content and choose low-sugar or homemade alternatives like tomato salsa, herbed yoghurt dip, green chutney etc.
8. High-Sugar Cereals
Many breakfast cereals are marketed as healthy but are often loaded with added sugars. Opt for classic varieties of whole-grain, low-sugar cereals or oatmeal and load it up with a mix of low GI fresh fruits, nuts and seeds for a healthier start to your day.
9. Alcohol
Alcohol can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels and should be consumed in moderation. It's essential to monitor your blood sugar when drinking and consider choosing light beer, dry wine, or spirits mixed with sugar-free mixers.
Conclusion
Effective diabetes management involves being aware of plating a balanced meal suitable to your body needs. Opting for healthier alternatives can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risks associated with diabetes. It's essential to seek guidance from healthcare professionals or dietitians to create a personalised diabetes management plan that suits your unique needs and goals.
Diabetes Management
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
Diabetic Nephropathy: Are Your Kidneys At Risk?
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of prolonged diabetes that can lead to kidney damage and even kidney failure. Diabetics need to be aware of their risk of developing diabetic nephropathy and take steps to prevent it.

Diabetes Management
Somogyi Effect: What Does That Early Morning Blood Sugar Spike Mean?
The Somogyi effect refers to a phenomenon where blood sugar levels drop too low during the night, triggering a compensatory release of hormones that raise blood sugar levels. This can lead to a serious blood sugar spike in the early morning. Some of the symptoms are night sweats, nightmares, evening weakness, and unexplained high morning blood sugar levels.

Diabetes Management
Can One Develop Diabetes at a Young Age?
Diabetes is not limited to older age, people can develop the condition at a young age too. Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, is an autoimmune condition, while Type 2 diabetes, increasingly affecting young people, is often linked to obesity and lifestyle factors. Risk factors include family history, obesity, sedentary behaviour, an unhealthy diet, and hormonal changes during puberty. Prevention and management involve a healthy lifestyle, regular check-ups, family support, and education about diabetes risks. It's crucial to recognise that diabetes can affect individuals of all ages, including teenagers and even children.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Diabetic Nephropathy: Are Your Kidneys At Risk?
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication of prolonged diabetes that can lead to kidney damage and even kidney failure. Diabetics need to be aware of their risk of developing diabetic nephropathy and take steps to prevent it.

Diabetes Management
Somogyi Effect: What Does That Early Morning Blood Sugar Spike Mean?
The Somogyi effect refers to a phenomenon where blood sugar levels drop too low during the night, triggering a compensatory release of hormones that raise blood sugar levels. This can lead to a serious blood sugar spike in the early morning. Some of the symptoms are night sweats, nightmares, evening weakness, and unexplained high morning blood sugar levels.

Diabetes Management
Can One Develop Diabetes at a Young Age?
Diabetes is not limited to older age, people can develop the condition at a young age too. Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, is an autoimmune condition, while Type 2 diabetes, increasingly affecting young people, is often linked to obesity and lifestyle factors. Risk factors include family history, obesity, sedentary behaviour, an unhealthy diet, and hormonal changes during puberty. Prevention and management involve a healthy lifestyle, regular check-ups, family support, and education about diabetes risks. It's crucial to recognise that diabetes can affect individuals of all ages, including teenagers and even children.