General Health
Scared To Travel Because Of Motion Sickness? These Tips May Help!
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 09 June 2022, Updated on - 17 June 2023
Share this article
0
82 likes
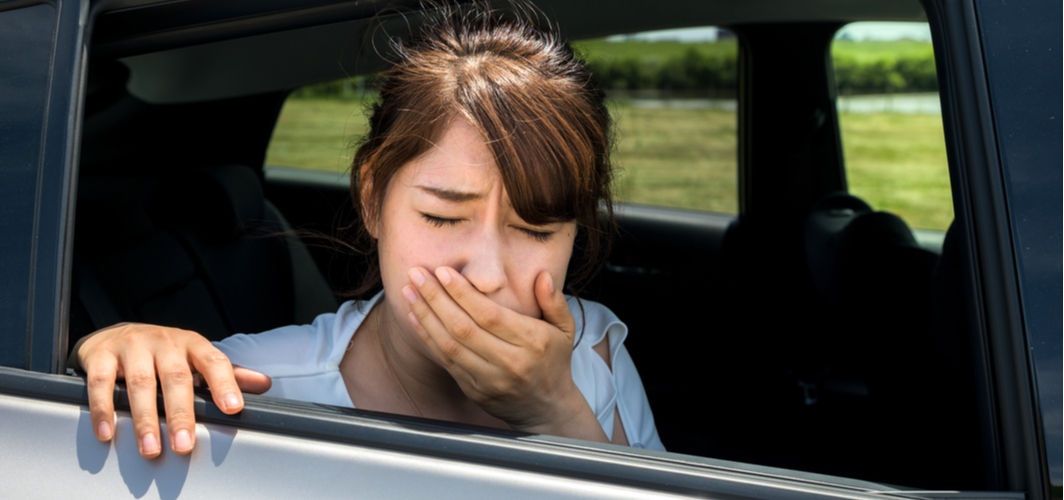

Many people experience dizziness, nausea, and headaches while travelling in a car, train, or aeroplane. These symptoms are caused by a common problem called motion sickness. While the ailment is not life-threatening, it can make travelling unpleasant and frustrating. Since most people vulnerable to motion sickness are aware of their status, following simple preventive measures can help them avoid the nagging symptoms. The article below explores how to deal with the symptoms of motion sickness in detail.
Science Behind Motion Sickness
Motion sickness is a common syndrome that is triggered upon subjection to various types of motion. It occurs primarily while travelling in a car, train, aeroplane, or boat. While nausea and vomiting are the most common symptoms of motion sickness, some people may also experience an upset stomach, headache, and irritability.
Recommended Read: When Should a Headache Worry You?
What causes motion sickness?
Motion sickness occurs when your brain receives conflicting signals from motion-sensing parts: the eyes, ears, muscles, and joints. To explain this in a better way, let’s suppose, you are traveling in a bus. Your eyes see trees and buildings passing by and recorded this as a movement. Similarly, your inner ears sense motion. However, your muscles and joints don’t experience movement as they are stationary. This imbalance between the signals sent by the motion-sensing parts confuses your brain as to whether you are stationary or moving. The resulting confusion leads to symptoms of motion sickness.
What are the symptoms of motion sickness?
Motion sickness can surprise you by striking without any forewarning. Some of the early signs of motion sickness are cold sweats, upset stomach, and nausea. Other common symptoms are:
- Dizziness
- Headache

- Fatigue
- Pale skin
- Irritability
- Difficulty in concentrating
- Increase in saliva production
- Rapid or shallow breathing
- Difficulty in maintaining balance
Who Is at Risk of Motion Sickness?
Motion sickness can affect just anyone. However, children aged 2 to 12 years, pregnant women, and older people could be at increased risk. Furthermore, factors that may increase the odds of motion sickness are:
- Family history of motion sickness
- Inner ear disorders
- Migraines
- Menstruation
- Hormonal birth control
- Parkinson’s disease
How to Prevent Motion Sickness?
If you are susceptible to motion sickness, following these preventive measures may lower your chances of getting sick or relieve symptoms if they occur:
- Don’t eat a large meal before or during travel. Only consume small portions of food.
- Avoid the consumption of oily, spicy, or acidic foods.

- Keep yourself hydrated by drinking at least 2 litres of water.
- Quit smoking and avoid exposure to second-hand smoke.
- Avoid consuming alcoholic beverages before or during the trip.
- If you are travelling in a car, choose the front passenger seat.
- Use the air-conditioner or roll down the window to get plenty of air.
- If you are travelling in an aeroplane, choose a seat that is close to the wing.
- While on a train, opt for a forward-facing seat.
- Don’t read while travelling in a car, aeroplane, or boat. Try to look out of the window at an object in the distance or towards the horizon.
- Intake of raw ginger and peppermint can also help ease symptoms.

- If possible, lie down when you experience nausea or any other symptom.
Can motion sickness be treated?
There is no definite treatment for motion sickness, however, some of the frequently prescribed medicines are:
- Dimenhydrinate
- Scopolamine
- Cyclizine
- Meclizine
- Promethazine
Most of these medications only prevent or ease the symptoms and can also induce sleepiness. It is advised to avoid driving or operating any kind of machinery after taking these medications.
Still worried,
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
General Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
General Health
Methylcobalamin Injection: Strategies for Effectively Managing Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Explore how to effectively manage and treat vitamin B12 deficiency through diet, supplements (methylcobalamin injection) and lifestyle changes.
General Health
Eye Flu In Delhi: Know The Causes, Symptoms And Ways To Treat Conjunctivitis
Eye flu results in inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye. Know the cause, types, treatment and ways to prevent conjunctivitis.

General Health
Five Effective Ways To Deal With High Cholesterol!
High cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart diseases and stroke. This article addresses how one can determine and deal with excess cholesterol.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Plant-based Foods That Are a Great Source of Iron
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
Methylcobalamin Injection: Strategies for Effectively Managing Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Explore how to effectively manage and treat vitamin B12 deficiency through diet, supplements (methylcobalamin injection) and lifestyle changes.

General Health
Eye Flu In Delhi: Know The Causes, Symptoms And Ways To Treat Conjunctivitis
Eye flu results in inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye. Know the cause, types, treatment and ways to prevent conjunctivitis.

General Health
Five Effective Ways To Deal With High Cholesterol!
High cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart diseases and stroke. This article addresses how one can determine and deal with excess cholesterol.