Diabetes Management
How Many Steps Should You Walk to Manage Your Diabetes?
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 04 October 2023
Share this article
0
0 like

Walking is a simple yet highly effective form of exercise that can play a significant role in managing blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes. It's a relatively easy activity that can be tailored to various fitness levels and can be easily incorporated into daily routines. Let’s delve deep to understand how many steps should people with diabetes aim for to reap the benefits of improved blood sugar control.
What are the Benefits of Walking for People with Diabetes?
Before delving into the number of steps, let’s understand why walking is beneficial for individuals with diabetes:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Regular walking can enhance the body's sensitivity to insulin, allowing better regulation of blood sugar levels. This effect can last for hours after a walk.
- Blood Sugar Control: Physical activity, including walking, can help lower blood sugar levels. It encourages the muscles to take up glucose from the bloodstream, reducing overall glucose levels in the blood.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for diabetes management. Walking aids in weight loss or maintenance, reducing the risk of insulin resistance associated with excess body fat.
- Heart Health: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease. Walking can improve cardiovascular fitness, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of heart-related complications.
How Many Steps Should You Target?
While there's no one-size-fits-all answer to the ideal number of steps for managing blood sugar levels, health organisations often recommend aiming for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. Walking can be a significant part of this recommendation.
Is Completing 10,000 Steps Actually Important?
You may have heard that aiming for 10,000 steps per day is an optimal target for overall health, including diabetes management. While this can be a helpful goal, it's not a strict requirement. Some individuals may need more or less depending on their fitness level and diabetes management goals.
Individualised Approach
The right number of steps varies from person to person. Factors like age, fitness level, overall health, and diabetes type influence the ideal step count. It's advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or a certified diabetes educator who can help you set specific goals tailored to your needs.
How to Get Started?
To ensure a smooth start and reap the maximum benefits, here are some essential guidelines to follow as you begin your journey:
- Gradual Progression: If you're new to exercise, start with a manageable number of steps and gradually increase it over time. Consistency is the key.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Pay attention to how your body responds to walking. Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels to understand the impact of your activity.
- Safety First: Ensure you have appropriate footwear, stay hydrated, and consider walking with a friend or carrying glucose tablets if you are at risk of low blood sugar.
Conclusion
Walking is an excellent way to manage blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes. While there isn't a universal step count, the goal is to engage in regular, moderate-intensity walking as part of an overall diabetes management plan. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the right approach for you and remember that consistency is key to reaping the benefits of walking for diabetes control.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
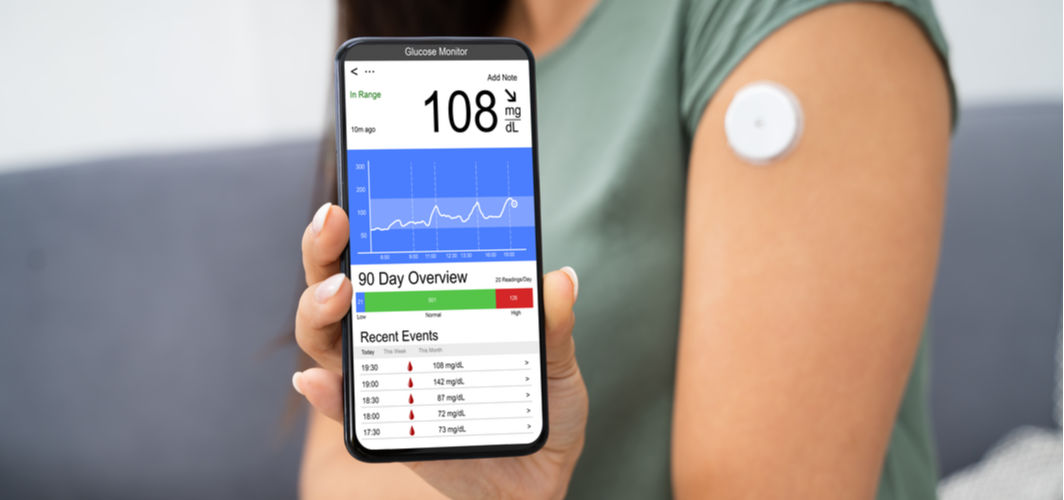
Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.
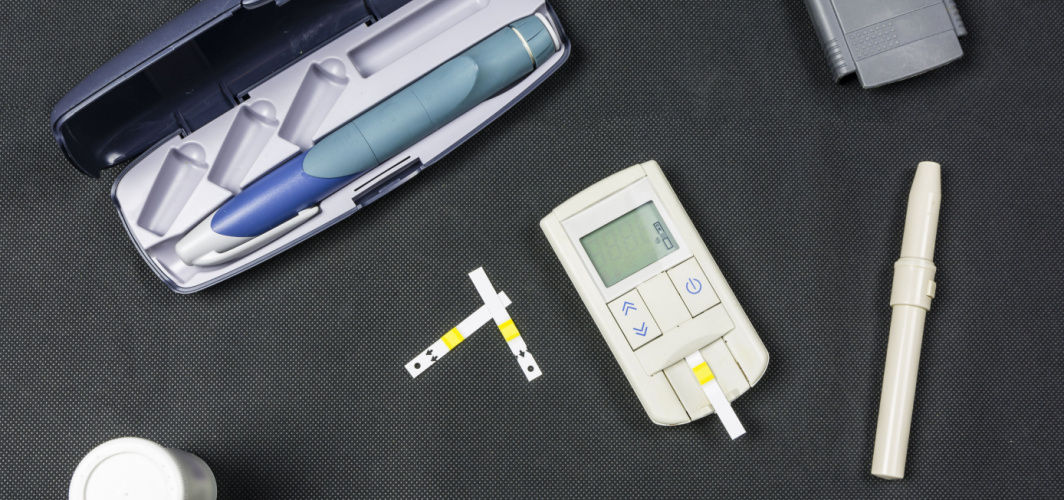
Diabetes Management
What Do Diabetes Test Packages Include?
A glucose random test is a simple procedure that requires no overnight fasting or any special preparations. It simply involves pricking the finger to obtain a drop of blood, which is placed on a test strip of a glucometer for blood glucose reading. A sugar level of 140 mg/dL or below is generally considered normal. This test provides a quick assessment of blood sugar levels without the need for fasting or specific timing.

Diabetes Management
Vision Troubles in Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment
While diabetes raises the chances of several eye-related complications, it can easily be managed with early diagnosis and proper treatment. Regular eye exams are vital for the early detection of conditions like macular edema, diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Diagnosis involves retinal imaging, comprehensive exams, visual acuity testing to measure the ability of the eye to differentiate shapes and details of objects at a given distance, and tonometry to measure intraocular pressure. Treatment options include blood sugar control, medications, laser therapy, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.

Diabetes Management
What Do Diabetes Test Packages Include?
A glucose random test is a simple procedure that requires no overnight fasting or any special preparations. It simply involves pricking the finger to obtain a drop of blood, which is placed on a test strip of a glucometer for blood glucose reading. A sugar level of 140 mg/dL or below is generally considered normal. This test provides a quick assessment of blood sugar levels without the need for fasting or specific timing.

Diabetes Management
Vision Troubles in Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment
While diabetes raises the chances of several eye-related complications, it can easily be managed with early diagnosis and proper treatment. Regular eye exams are vital for the early detection of conditions like macular edema, diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Diagnosis involves retinal imaging, comprehensive exams, visual acuity testing to measure the ability of the eye to differentiate shapes and details of objects at a given distance, and tonometry to measure intraocular pressure. Treatment options include blood sugar control, medications, laser therapy, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
