General Health
Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Beneficial For Diabetics?
7 min read
By Apollo Pharmacy, Published on - 05 September 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
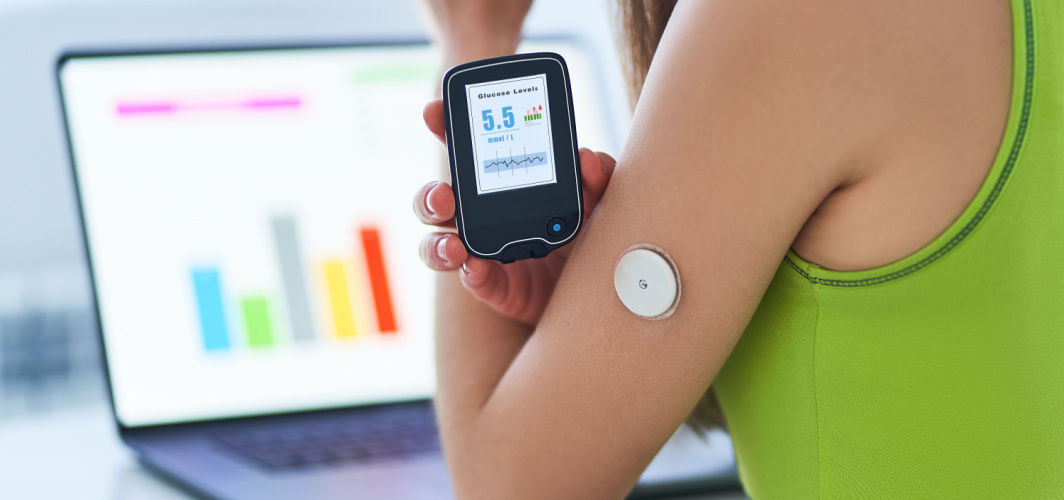
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems have revolutionised the way diabetes is managed. This technology has proven to be a game-changer in diabetes care, offering several advantages over conventional methods. Unlike traditional blood sugar monitoring, which involves periodic finger pricks, CGM provides real-time data on glucose levels, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise and medication. Read on to learn more about its benefits and usage.
What is a Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System?
A CGM system is a medical device that measures glucose levels in real time throughout the day and night. CGM systems consist of three main components:
- A small sensor: The sensor is inserted under the skin to measure interstitial fluid glucose levels.
- Transmitter: The transmitter wirelessly sends the data from the sensor
- A receiver or smartphone app: The receiver or the app receives the data from the transmitter, where the user can view their glucose values in real time.
Types of CGM Systems
There are several types of CGM systems available in the market, each with its own set of features and benefits. Here are some commonly used CGM systems
1. Dexcom G6
Dexcom G6 system consists of a small sensor that lasts for up to 10 days, a slim transmitter and a touchscreen receiver or compatible smartphone app. It does not require fingerstick calibration and provides accurate glucose readings.
2. Freestyle Libre
Freestyle Libre system uses a small sensor that lasts up to 14 days and does not require fingerstick calibration. It also offers optional alarms for high or low glucose levels.
3. Medtronic Guardian Sensor 3
Medtronic Guardian Sensor 3 system integrates with Medtronic insulin pumps and automatically suspends insulin delivery when glucose levels are too low. It also provides predictive alerts for high or low glucose levels.
4. Eversense
Eversense CGM system uses an implantable sensor that lasts for up to 90 days. It can be easily removed and reinserted by a healthcare professional.
Benefits and Advantages of CGM Systems
CGM Systems offer numerous benefits and advantages for individuals with diabetes.
1. Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for effective diabetes management. Having real-time glucose data allows you to make more informed decisions about
- Food choices
- Medication dosages
- Physical activity
2. Improved Glycemic Control
One of the significant advantages of CGM systems is their ability to improve glycemic control.
- Studies have shown that using CGM devices can lead to a reduction in both high and low blood glucose excursions. This is because CGMs provide continuous glucose readings, allowing individuals to make immediate adjustments to their treatment plans.
- Research has also demonstrated that CGM use can significantly lower HbA1c levels. HbA1c is a measure of long-term glucose control, and a decrease in HbA1c indicates improved overall glycemic control.
- The American Diabetes Association (ADA) now recommends CGM use for certain groups, including individuals with type 1 diabetes and those on intensive insulin regimens.
3. Enhanced Safety and Hypoglycemia Prevention
One of the significant advantages of CGM is enhanced safety and hypoglycemia prevention.
- The continuous monitoring feature of CGM systems alerts users when their glucose levels are trending downward, enabling them to take preventive measures such as consuming glucose-rich foods or adjusting insulin doses.
- CGM systems have been shown to reduce the risk of severe hypoglycemia. These devices provide early warnings of impending hypoglycemic episodes, giving individuals ample time to intervene and prevent the occurrence of dangerously low blood sugar levels.
How to Incorporate CGM into Your Daily Life?
Integrating CGM into daily life may require some lifestyle adaptations.
1. Tips to Incorporate CGM Seamlessly
Tips for wearing and maintaining a CGM device comfortably:
- Choose a site for sensor placement that is convenient and comfortable for you. Common sites include the abdomen, upper arm or buttocks.
- Clean the area properly before inserting the sensor to reduce the risk of infection.
- Ensure that the adhesive patch is secure to prevent the sensor from falling off or becoming dislodged.
- Avoid using lotions, oils or creams on the site as they can interfere with the sensor's accuracy.
2. Nutrition and Meal Planning with CGM Systems
For managing blood glucose levels with CGM systems, nutrition and meal planning plays a crucial role.
- Consistency is key: Stick to a regular eating pattern with consistent meal times. This helps in maintaining stable blood glucose levels throughout the day.
- Choose complex carbohydrates: Instead of refined sugars and simple carbs, opt for whole grains, fruits and vegetables. These provide a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing rapid fluctuations.
- Portion control: Pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating. Smaller, frequent meals can be beneficial for better glycemic control.
- Fibre-rich foods: Include foods high in fibre, such as whole grains, legumes and vegetables, which help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Limit processed foods and sugary beverages: These can cause sharp spikes in blood sugar levels, making it difficult to manage glucose effectively.
3. Common Concerns with CGM System
Common concerns or challenges with CGM usage include the following:
- Skin irritation: If you experience skin irritation from the adhesive patch, try using a barrier spray or cream recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Signal loss: In case of signal loss between the CGM device and receiver/smartphone, ensure that they are within proximity. You can also consider using signal extenders or Bluetooth range boosters if needed.
- Calibrating the sensor: Follow your healthcare provider's instructions for calibrating your CGM device accurately. This will help ensure accurate glucose readings.
How to Choose the Right CGM System?
There are several factors to consider while choosing a CGM system.
- Cost: CGM systems can vary in price, so it is important to consider your budget.
- Accuracy: Look for a CGM system that offers reliable and accurate readings.
- Compatibility: Make sure the CGM system you choose is compatible with your current insulin pump or diabetes management device, if applicable. This will ensure seamless integration and data sharing.
It is also important to consider recommendations based on different age groups and lifestyles. For example:
- For children and teenagers: Look for CGM systems that are user-friendly and have features tailored to their needs, such as alarms and alerts for low or high blood sugar levels.
- For athletes or individuals with an active lifestyle: Consider CGM systems that are designed for continuous wear during physical activity without compromising accuracy or comfort.
How to Use the CGM System?
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you with the insertion and calibration process of a CGM system:
Step 1: Clean the area
Before inserting the CGM sensor, make sure to clean the site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry completely.
Step 2: Insert the sensor
Follow the manufacturer's instructions to insert the sensor under the skin. Be gentle and avoid applying excessive force.
Step 3: Attach the transmitter
Once the sensor is in place, attach the transmitter to it. Ensure that it is securely attached.
Step 4: Calibrate the CGM
After the initial warm-up period mentioned by the manufacturer, you will need to calibrate the CGM system using a fingerstick blood sugar measurement. Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare professional or as per the device guidelines.
Troubleshooting common issues during set-up involves the below:
- Sensor error: If you encounter a sensor error message, try reinserting the sensor after checking for any visible issues like kinks or damage.
- Inaccurate readings: If you notice inconsistent readings, ensure that your hands are clean before calibrating and that you follow proper calibration techniques.
- Skin irritation: Some individuals may experience skin irritation at the sensor site. If this occurs, consult your healthcare professional for guidance on managing skin reactions.
Conclusion
CGM systems are a game-changer in diabetes care, offering several benefits. By adopting CGM systems that provide accurate information about blood sugar trends, individuals can gain better insights into their blood sugar levels, identify triggers for high or low glucose levels, and make timely interventions to maintain optimal health. Its convenience, accuracy, and ability to provide real-time insights make it worth exploring. Talk to your healthcare provider about whether continuous glucose monitoring is right for you.
Explore Blood Glucose Monitors
FAQs
Q. Are CGM systems accurate?
CGM systems have evolved over the years, and the latest models offer high levels of accuracy.
Q. Can CGM systems replace fingerstick testing?
While CGM systems provide valuable real-time information, fingerstick testing is still required for calibration and confirming glucose levels.
Q. How often should I change the sensor?
Sensor lifespan varies among different devices, but most need replacement every 7-14 days. Regular sensor changes ensure accuracy and prevent skin irritation.
Q. Are CGM systems suitable for children?
Yes, CGM systems are suitable for both adults and children.
Q. Can I exercise or bathe with a CGM system?
CGM systems are waterproof and can withstand activities like swimming and bathing.
General Health
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

General Health
Five Reasons That Will Make You Fall In Love With Dark Chocolates!
Eating dark chocolate is linked to multiple health benefits, including improved heart health, better cognitive function, reduced stress, increased workout performance and lower risk of type 2 diabetes.

General Health
How Can Facial Yoga Exercise Help You Stay Young?
We live in a world where the only things we do are things like consume fast food, get too little sleep, and not take care of our facial skin, all of which can make us look older. It causes wrinkles, fine lines, sagging skin, and other skin issues like that. You can alleviate this problem by engaging in facial yoga exercises. Check out this blog.
General Health
Essential Vaccines And Boosters For Every Adult
Explore the vital vaccines and boosters essential for adult well-being. Prioritise your health and protect your community.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

The Best Exercises for Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
Five Reasons That Will Make You Fall In Love With Dark Chocolates!
Eating dark chocolate is linked to multiple health benefits, including improved heart health, better cognitive function, reduced stress, increased workout performance and lower risk of type 2 diabetes.

General Health
How Can Facial Yoga Exercise Help You Stay Young?
We live in a world where the only things we do are things like consume fast food, get too little sleep, and not take care of our facial skin, all of which can make us look older. It causes wrinkles, fine lines, sagging skin, and other skin issues like that. You can alleviate this problem by engaging in facial yoga exercises. Check out this blog.

General Health
Essential Vaccines And Boosters For Every Adult
Explore the vital vaccines and boosters essential for adult well-being. Prioritise your health and protect your community.
