Diabetes Management
To Avoid Health Complications, This Is How Frequently You Should Check Your Blood Glucose
4 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 06 June 2022, Updated on - 18 September 2023
Share this article
0
63 likes

Testing blood glucose levels is a part and parcel of life for people with diabetes. However, there are many who do not understand the significance of checking fasting and postprandial (after meal) blood glucose levels. Experts say it is important to keep track of your blood glucose levels to avoid complications. But what should be the ideal frequency for testing the glucose levels? The article below answers this question in detail.
Why is it important to check your blood glucose levels regularly?
Regularly testing blood glucose levels can help reveal essential information for the management of diabetes. It can help you:
- Determine whether your blood glucose levels are high or low
- Assess the impact of diabetes medication on your blood glucose levels
- Monitor your progress in achieving your diabetes management goals
- Understand the effects of diet and physical activity on your blood glucose levels
- Evaluate how stress, illness, injury, menopause, etc affect your blood glucose levels
What is the right time to get your blood glucose levels checked?
The frequency of the tests to measure your blood glucose levels usually depends on the diabetes type and your treatment regimen.
1. Type 1 Diabetes: If you have type 1 diabetes then you may have to test your blood glucose levels four to ten times a day. You may have to test your levels:
- Before meals
- Before and after physical activity
- Before going to sleep
- During the night (occasionally)
Sometimes, you may have to test more often if you are ill, have made certain changes to daily regimen, or have started taking new medication.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
People suffering from type 2 diabetes may not require regular blood glucose testing if they are managing the levels effectively with the help of medication, diet and exercise. On the other hand, if the person is using insulin to manage diabetes, then the physician may recommend testing multiple times a day. However, the frequency of testing depends on the type and amount of insulin that you use.
If you are taking multiple insulin shots over the course of the day, blood glucose testing is usually recommended before meals and at bedtime. Those taking intermediate or long-acting insulin may only have to test their blood glucose levels prior to breakfast and before going to bed.
What should be your target blood glucose levels?
Generally, the target blood glucose levels should be:
- Fasting (before meals): 80 to 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
- After having a meal: Not more than 180 mg/dL
However, your target blood glucose range can vary from the aforementioned range. Factors that may affect your target range include:
- Type and severity of diabetes
- Age
- Duration of your diabetes
- Your pregnancy states
- Preexisting diabetes complications
- Presence of other chronic conditions
People aged 60 years and above and those with serious medical conditions such as heart disease, kidney disease, or lung disease may have slightly higher target blood glucose level goals.
How to maintain healthy blood glucose levels?
It is quintessential to follow a nutritious, low-calorie diet in order to keep fasting blood glucose levels under control. Some of the steps that can help you maintain your levels within the target range include:
- Reduce intake of sugar and sodium (salt)

- Replace processed foods with whole grains
- Consume more fibre, protein-rich, and non-starchy vegetables such as broccoli, cucumber, carrots, and cauliflower.
However, it is also important to ensure that your blood glucose levels do not fall dangerously low. Therefore, you must follow certain measures to prevent a steep decline in your blood glucose level:
- Have small, regular meals throughout the day
- Increase food intake if you exercise
- Limit intake of alcoholic beverages

- Talk to a physician if a pre-existing condition is making it difficult to control blood glucose levels
If you have diabetes, testing blood glucose levels is crucial for you. Testing can inform you whether your blood glucose levels are within the normal range. It can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of medications, diet, and exercise in managing diabetes. Once you know how many times you need to get tested, you must ensure that your blood glucose levels remain within the target range. It must be noted that every diabetic can have a different target range, therefore, you must consult your physician for the same.
You can also manage your diabetes like a pro with Apollo 24|7's 12-week empower programme.
Diabetes Management
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Five Essential Tips for Diabetes Self-Management
Managing diabetes effectively involves regular blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, exercise, medication adherence, stress management, and self-care. These five essential tips empower individuals to take control of their diabetes, whether it's Type 1, Type 2, or Gestational Diabetes. By monitoring blood sugar levels, understanding dietary choices, staying active, adhering to prescribed medications, and managing stress, individuals can lead healthier, happier lives with reduced complications. Diabetes management requires dedication, but the improved health outcomes make it a worthwhile effort.

Diabetes Management
Debunking 5 Common Myths About Diabetes
Having a family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes in individuals. However, many people develop diabetes without any of their family members having the condition. Lifestyle factors like being obese or overweight, prediabetes, PCOS, gestational diabetes, and age above 45 can also be contributing factors. To reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a healthy diet is important.
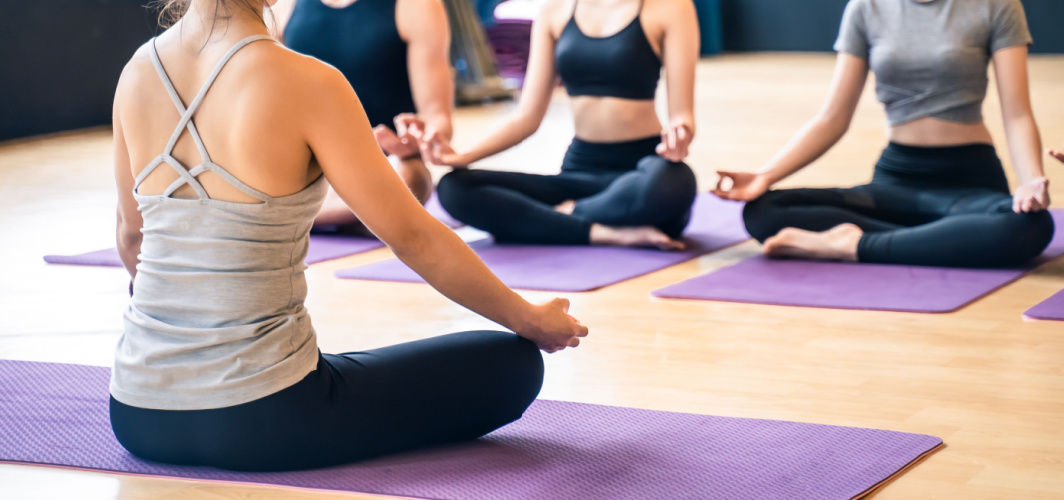

Diabetes Management
5 Best Exercises To Manage Diabetes
Five exercises that are best for managing diabetes are walking, strength training, swimming, yoga and High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT). Walking can help lower blood sugar levels, make your heart healthier, and help you manage your weight. Strength training like squats, lunges, presses, rows, and planks can improve insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular health. Swimming keeps your overall body fit, while yoga can help reduce stress and anxiety. HIIT can enhance insulin utilization and cardiovascular fitness.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Five Essential Tips for Diabetes Self-Management
Managing diabetes effectively involves regular blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, exercise, medication adherence, stress management, and self-care. These five essential tips empower individuals to take control of their diabetes, whether it's Type 1, Type 2, or Gestational Diabetes. By monitoring blood sugar levels, understanding dietary choices, staying active, adhering to prescribed medications, and managing stress, individuals can lead healthier, happier lives with reduced complications. Diabetes management requires dedication, but the improved health outcomes make it a worthwhile effort.

Diabetes Management
Debunking 5 Common Myths About Diabetes
Having a family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes in individuals. However, many people develop diabetes without any of their family members having the condition. Lifestyle factors like being obese or overweight, prediabetes, PCOS, gestational diabetes, and age above 45 can also be contributing factors. To reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a healthy diet is important.

Diabetes Management
5 Best Exercises To Manage Diabetes
Five exercises that are best for managing diabetes are walking, strength training, swimming, yoga and High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT). Walking can help lower blood sugar levels, make your heart healthier, and help you manage your weight. Strength training like squats, lunges, presses, rows, and planks can improve insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular health. Swimming keeps your overall body fit, while yoga can help reduce stress and anxiety. HIIT can enhance insulin utilization and cardiovascular fitness.