Heart Conditions
Arrhythmia: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment & Prevention
8 min read
By Apollo Pharmacy, Published on - 19 October 2023, Updated on - 16 September 2025
Share this article
0
12 likes

The heart beats in a regular and coordinated manner in a healthy individual, allowing blood to be pumped efficiently throughout the body. However, when someone experiences arrhythmia, the heart's electrical signals become disrupted, causing it to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. It can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Identifying and discussing arrhythmia symptoms with a doctor is important for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Understanding cardiac arrhythmia is crucial because it affects millions of people worldwide, including many in India.
What is Arrhythmias?
Arrhythmias refer to abnormal heart rhythms, where the heart may beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregularly. The heart's normal rhythm is controlled by the electrical system, which coordinates the contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle. When there is a disruption in this electrical system, it can lead to arrhythmias.
Types of Arrhythmias
Understanding the different types of arrhythmias is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They can be effectively managed through various arrhythmia treatment options. Here are the main types of arrhythmias.
1. Sinus Node Dysfunction
Sinus node dysfunction occurs when the heart's natural pacemaker, the sinus node, does not function properly. There are two main subtypes:
- Sinus Bradycardia: In this condition, the heart beats slower than normal, with a resting heart rate below 60 beats per minute.
- Sinus Tachycardia: Characterised by a faster-than-normal heart rate, the heart beats typically above 100 beats per minute at rest.
2. Atrial Arrhythmia
Atrial arrhythmia symptoms occur when there is an abnormal electrical activity in your atria, the upper chambers of your heart. The two common types include:
- Atrial Fibrillation: A rapid and irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke.
- Atrial Flutter: Atrial flutter is characterised by a fast but regular heartbeat.
3. Ventricular Arrhythmias
Ventricular arrhythmias occur when there are abnormal electrical signals in the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart. Two significant types include:
- Ventricular Tachycardia: This condition involves rapid and irregular heartbeats originating from the ventricles. It may require immediate medical intervention.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: Characterised by chaotic electrical activity in the ventricles, ventricular fibrillation causes the heart to quiver instead of pumping effectively. It can be life-threatening.
Causes of Arrhythmia
Understanding arrhythmia causes is crucial for early detection and for the prescription of appropriate arrhythmia treatment medications.
1. Heart Conditions
Arrhythmias can occur because of various underlying heart conditions. Some conditions include:
- Coronary Artery Disease: This is caused by the build-up of plaque in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. The reduced blood flow can disrupt the heart's electrical system.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Structural abnormalities present at birth can affect the heart's rhythm by disrupting electrical signals.
- Heart Valve Problems: Malfunctioning heart valves can lead to abnormal blood flow and cause arrhythmias.
2. Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors and external triggers can contribute to the development of arrhythmias. These include:
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect the heart's electrical system.
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can disrupt the heart's rhythm and trigger arrhythmias.
- Stimulants Such as Caffeine: Excessive amounts of caffeine or other stimulants can stimulate the heart and lead to irregular heart rhythms.
3. Medical Conditions and Medication
Certain medical conditions and medications can be among the arrhythmia causes. These include:
- Thyroid Disorders: Overactive or underactive thyroid function can disrupt the heart's electrical system.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Imbalances in essential minerals like potassium, calcium, or magnesium can affect the heart's electrical activity, resulting in arrhythmias.
- Certain Medications: Certain antibiotics and antidepressants have been associated with increasing the risk of arrhythmias.
Symptoms and Signs of Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia often presents with a range of symptoms. It is important to recognise these signs of arrhythmia to seek prompt medical attention. Common arrhythmia symptoms include:
- Palpitations or Irregular Heartbeat: A sensation of skipped heartbeats, fluttering, or a rapid, pounding heartbeat.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Arrhythmia can cause reduced blood flow to important organs, leading to feelings of fatigue and weakness.
- Dizziness or Fainting Spells: If the heart's rhythm becomes too fast or too slow, it can disrupt blood flow to the brain, resulting in dizziness or fainting.
- Shortness of Breath in Atrial Fibrillation: Atrial fibrillation can lead to an irregular and rapid heartbeat, reducing the heart's ability to pump blood effectively, resulting in shortness of breath.
- Chest Pain in Ventricular Arrhythmias: Ventricular arrhythmias can cause chest pain or discomfort due to inadequate blood supply to the heart muscle.
Tests That Aid in the Diagnosis of Arrhythmia
Your doctor will take your medical history to understand your arrhythmia symptoms and to determine underlying conditions that may contribute to arrhythmia. They will also perform physical examinations to check your heart rate, rhythm, and any signs of abnormality. Some tests include:
1. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
A common and non-invasive test, ECG records the electrical activity of your heart. It identifies abnormal heart rhythms and provides information about the type and severity of arrhythmia.
2. Holter Monitoring and Event Recorders
Holter monitoring involves wearing a portable device that continuously records your heart's electrical activity for 24-48 hours or longer. Event recorders, used for shorter periods, allow you to record readings when you experience symptoms.
3. Electrophysiology Study (EPS)
An invasive procedure that involves inserting catheters into your blood vessels and mapping your heart's electrical signals. EPS helps locate the source and determine appropriate arrhythmia treatment medication.
4. Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of your heart's structure and function.
Other imaging tests like MRI or CT scans can also assess structural abnormalities or damage to the heart.
Treatment Options for Arrhythmia
The treatment and management of arrhythmias depend on the type of arrhythmia, its underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and the overall health of the individual.
1. Medications
Arrhythmia treatment medications can control symptoms and prevent complications.
- Beta-blockers and Calcium Channel Blockers: These medications help slow down the heart rate, reducing the frequency and intensity of irregular heart rhythms.
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Antiarrhythmic medications are used to restore normal heart rhythm by slowing down electrical impulses and stabilising the heart's electrical activity.
2. Procedures and Interventions
For more severe cases, arrhythmia treatment with procedures or interventions may become necessary.
- Catheter Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure using radiofrequency energy to destroy abnormal heart tissue responsible for causing arrhythmias.
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): An ICD is implanted to check heart rhythm and deliver electric shocks to restore normal rhythm if necessary.
- Pacemaker Implantation: Pacemakers are devices implanted under the skin to regulate the heart's electrical signals, ensuring a steady and regular heartbeat.
Preventive Measures for Arrhythmia
Maintaining a healthy heart is crucial in arrhythmia prevention. Two key habits that can help are the following:
1. Regular Exercise Routine
Exercise helps improve blood circulation, strengthen the heart muscle, and reduces the risk of arrhythmia. Aim for moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, yoga for heart health, for at least 30 minutes on most days of the week.
2. Balanced Diet with Heart-healthy Foods
Include heart-healthy foods such as lean proteins, fruits, whole grains, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products in your meals.
3. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Intake
Smoking damages blood vessels and the heart, increasing the risk of arrhythmia. Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the heart's rhythm.
4. Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on the heart and trigger arrhythmia. Practising stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises can reduce stress levels and minimise risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, arrhythmia is a condition characterised by abnormal heart rhythms. Symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, palpitations, and chest pain are signs of arrhythmia. There are several arrhythmia causes, including heart disease, high blood pressure, thyroid problems, and certain medications. Your doctor will prescribe arrhythmia treatment medications and recommend appropriate arrhythmia prevention measures. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage arrhythmia. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, managing stress levels, and avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption.
FAQS
Q. Can emotional stress cause arrhythmia?
Yes, emotional stress can trigger arrhythmia symptoms in some individuals. It can disrupt the electrical signals in the heart and lead to irregular heartbeats. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of arrhythmias.
Q. Is arrhythmia hereditary?
Arrhythmias can have a genetic component, meaning they can run in families. If you have a family history of arrhythmias or sudden cardiac death, it is important to discuss it with your healthcare provider.
Q. Is medication the only treatment option for arrhythmia?
Medication is one of the treatment options for arrhythmia, especially for managing symptoms and controlling heart rhythm. However, other treatments such as lifestyle changes, catheter-based procedures, and in some cases, surgery may be recommended.
Q. Can high blood pressure contribute to arrhythmia?
Yes, high blood pressure can increase the risk of developing arrhythmia. Keeping blood pressure and cholesterol levels under control and making positive lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of arrhythmia.
Q. Can arrhythmias be prevented?
In some cases, arrhythmias can be prevented by adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. Maintaining a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress levels, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use can help reduce risk factors.
Keep your heart healthy by understanding arrhythmia. Learn its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Heart Conditions
Consult Top Cardiologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Heart Conditions
Dietary Fats: What's Good for Your Heart?
While some dietary fats offer certain health benefits when consumed in moderation, others have been linked to negative health effects. Knowing the difference can help people make the right choice.

Heart Conditions
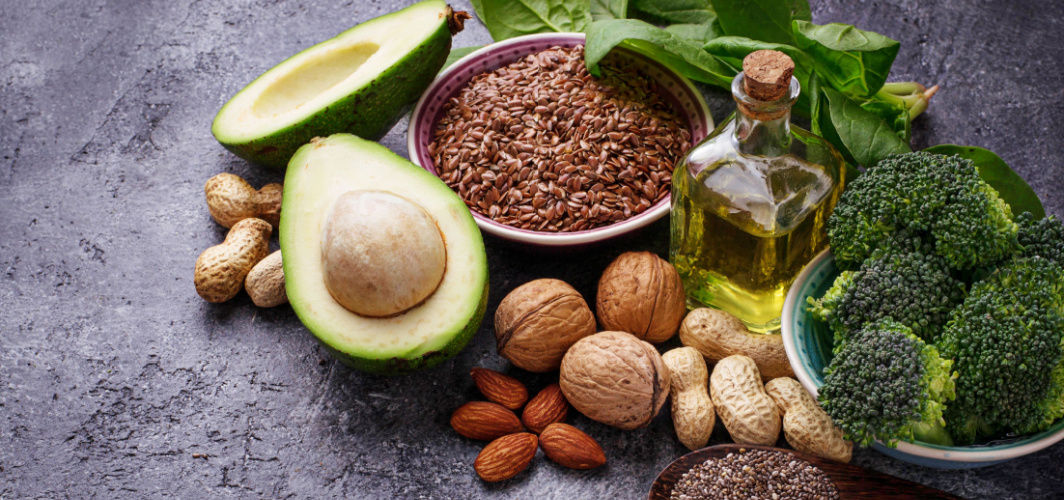
Keep Your Heart Healthy Naturally With These 5 Home Essentials
Our heart needs to work optimally to help it engage in all kinds of activities and hobbies. 5 essential ingredients/foods that help in maintaining and improving heart health include fatty fish, nuts and seeds, green leafy vegetables, olive oil, and avocados.
Heart Conditions
Why You Should Regularly Check Your Blood Pressure at Home
Both high and low blood pressure can be extremely dangerous and can result in serious health consequences. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor blood pressure frequently.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

7 Tips to Manage Hypertension
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Heart Conditions
Dietary Fats: What's Good for Your Heart?
While some dietary fats offer certain health benefits when consumed in moderation, others have been linked to negative health effects. Knowing the difference can help people make the right choice.

Heart Conditions
Keep Your Heart Healthy Naturally With These 5 Home Essentials
Our heart needs to work optimally to help it engage in all kinds of activities and hobbies. 5 essential ingredients/foods that help in maintaining and improving heart health include fatty fish, nuts and seeds, green leafy vegetables, olive oil, and avocados.

Heart Conditions
Why You Should Regularly Check Your Blood Pressure at Home
Both high and low blood pressure can be extremely dangerous and can result in serious health consequences. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor blood pressure frequently.
