Diabetes Management
Aerobic or Resistance Exercises: Which One is Ideal to Manage Blood Sugar?
4 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 25 November 2020, Updated on - 30 August 2023
Share this article
0
0 like

Aerobic exercise
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Jogging or running
- Cycling / stationary cycling
- Climbing stairs
- Dancing
What is interval aerobic training?
Resistance training
- Free weights (e.g., dumbbells)
- Weight machines
- Resistance bands
- Stretching exercises
- Muscle-building exercise
Which exercise is ideal for diabetic people?
Conclusion
Diabetes Management
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
Adding a Smile to Your Diabetes Management
Oral hygiene is crucial for diabetics. Diabetes increases the risk of gum diseases like tooth decay and cavities. Hence, regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential for diabetics to maintain good oral health and support overall well-being.

Diabetes Management
Can Regular Exercise Help Beat Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can be managed successfully with early detection and lifestyle changes. Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes must eat a healthy diet, stay physically active, regularly monitor blood glucose levels and follow their medications to manage gestational diabetes. They can also consult a dietitian for a balanced meal plan. Medications like metformin may be prescribed by doctors if needed.
Diabetes Management
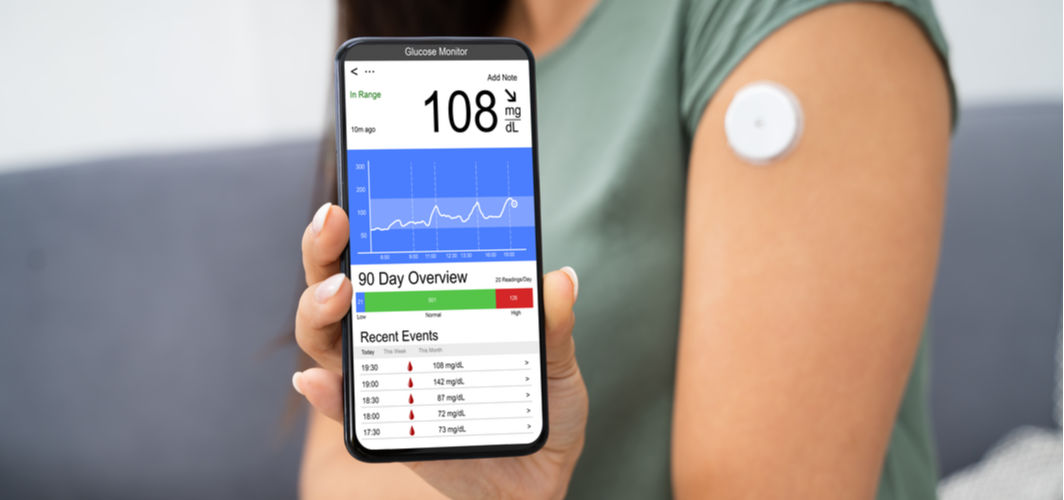
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Adding a Smile to Your Diabetes Management
Oral hygiene is crucial for diabetics. Diabetes increases the risk of gum diseases like tooth decay and cavities. Hence, regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential for diabetics to maintain good oral health and support overall well-being.

Diabetes Management
Can Regular Exercise Help Beat Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can be managed successfully with early detection and lifestyle changes. Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes must eat a healthy diet, stay physically active, regularly monitor blood glucose levels and follow their medications to manage gestational diabetes. They can also consult a dietitian for a balanced meal plan. Medications like metformin may be prescribed by doctors if needed.

Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.