Diabetes Management
Adding a Smile to Your Diabetes Management
2 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 18 October 2021, Updated on - 27 August 2023
Share this article
0
182 likes
Diabetes is a medical condition that requires a lifelong commitment to a healthy diet and lifestyle. While the role of diet in managing diabetes is pretty well known, the impact of a healthy lifestyle beyond regular physical activity on blood sugar levels is little understood. Many people would be surprised to know that even adding a smile to their daily routines can help them improve diabetes care.
Oral care is an important part of everyone’s daily routine. However, it is even more significant for people living with diabetes as they are at a greater risk for oral diseases. Experts say that poor oral care not only compromises the health of teeth and gums, but it can even complicate diabetes management. However, on a brighter note, it is possible to prevent these problems.
The article below explains the correlation between diabetes and oral care in detail.
Understanding the relationship between diabetes and oral care
High glucose levels (in blood and saliva) constitute a major link between diabetes and oral health. People with uncontrolled diabetes have very high levels of glucose in their saliva which helps foster the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth. These harmful bacteria combine with tiny food particles to create plaque (a soft and sticky substance) on the teeth. The acids in plaque damage the surfaces of teeth (enamel and dentin). Over time, this leads to cavities and gum disease.
Similarly, people living with diabetes are also at a greater risk for oral problems. High levels of glucose in blood levels significantly increase the risk of bacterial infection and adversely affects healing. High blood glucose levels also impair white blood cells that help fight bacterial infections. Moreover, severe gum disease can also spike blood glucose levels which makes it further difficult to manage diabetes.
Tips for better oral health and diabetes management
While the problems emanating from poor oral care and diabetes may sound serious, they are easy to prevent if effective measures are taken on time. Some of the simple tips that can help people living with diabetes improve their oral health and diabetes management are:
- Strive to maintain blood glucose levels within the target range
- Eat healthy meals and become physically active
- Brush and floss teeth properly at least twice daily
- Rinse mouth with antiseptic mouthwash at least once a day
- Quit smoking (for those who do)
- People who use dentures should clean them daily
- Visit a dentist for regular oral health check-ups.
Takeaway
Health experts recommend focussing on oral care for better diabetes management. Simple oral care techniques such as brushing, flossing, and rinsing with mouthwash are not only proven ways of improving oral health but also diabetes management. A lifelong commitment to these techniques will be rewarded with better health outcomes and a shining smile.
Explore our range of oral care products to maintain your smile and diabetes care.
You can also manage your diabetes like a pro with Apollo 24|7's 12-week empower programme.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
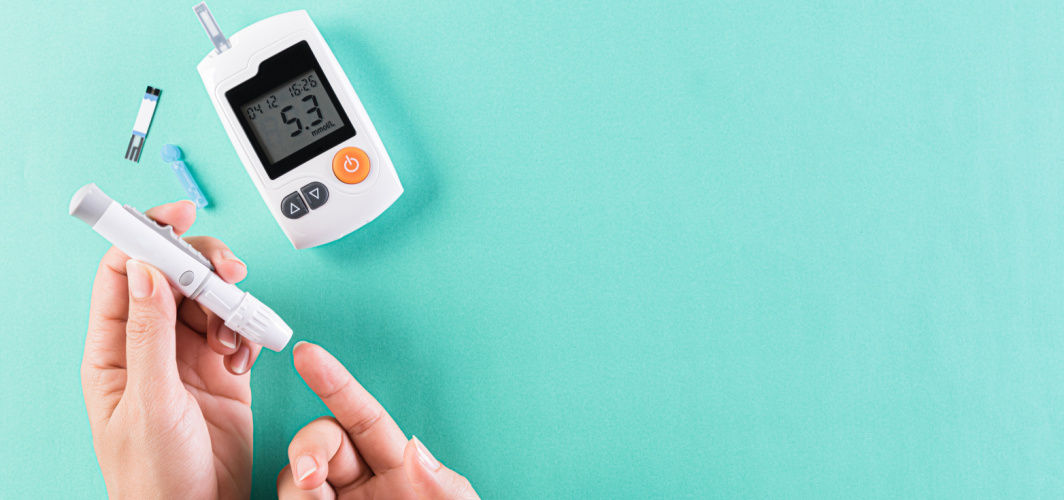

Diabetes Management
How Diabetes Can Affect Your Digestive System
Learn about the latest updates in guidelines, new technologies, and lifestyle factors to manage diabetes effectively. Discover valuable information on prevention, treatment, and living a healthy life with diabetes.

Diabetes Management
Does Gestational Diabetes Lead to Type 2 Diabetes?
After childbirth, blood sugar levels in the mother typically normalize within six weeks. However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 50% of women with gestational diabetes may develop type 2 diabetes later in life. The risk can be reduced by maintaining a healthy weight, making healthy food choices, and engaging in regular physical activity.
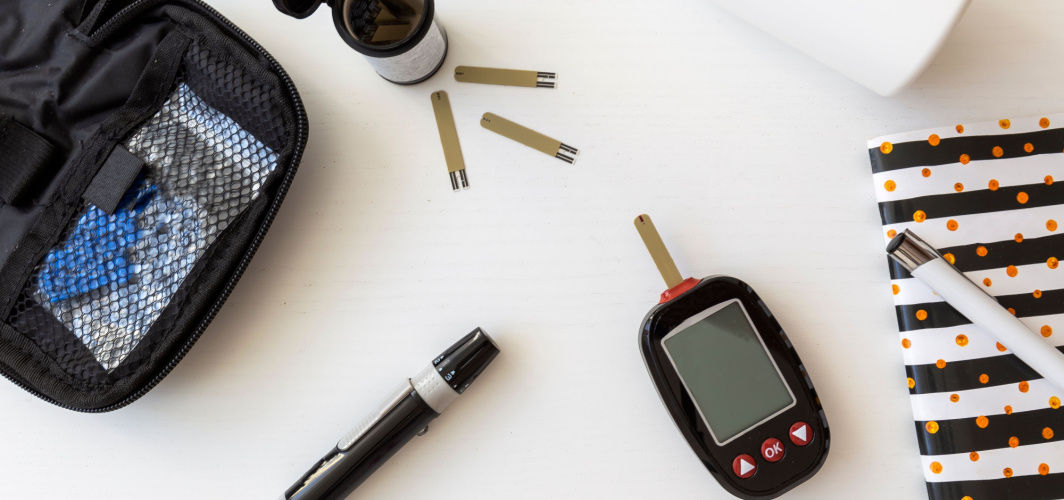

Diabetes Management
A Step-By-Step Guide To Using A Glucometer
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for effective diabetes management. Glucometers, portable devices that measure blood glucose levels at home, offer convenience. To use a glucometer, start by gathering necessary supplies: soap or alcohol prep pads, test strips, a lancing device with a new lancet, and a notepad or smartphone app to record results. Follow these steps: clean your hands, turn on the glucometer, prick your fingertip, apply blood to the test strip, stop bleeding, and record the results.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
How Diabetes Can Affect Your Digestive System
Learn about the latest updates in guidelines, new technologies, and lifestyle factors to manage diabetes effectively. Discover valuable information on prevention, treatment, and living a healthy life with diabetes.

Diabetes Management
Does Gestational Diabetes Lead to Type 2 Diabetes?
After childbirth, blood sugar levels in the mother typically normalize within six weeks. However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 50% of women with gestational diabetes may develop type 2 diabetes later in life. The risk can be reduced by maintaining a healthy weight, making healthy food choices, and engaging in regular physical activity.

Diabetes Management
A Step-By-Step Guide To Using A Glucometer
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for effective diabetes management. Glucometers, portable devices that measure blood glucose levels at home, offer convenience. To use a glucometer, start by gathering necessary supplies: soap or alcohol prep pads, test strips, a lancing device with a new lancet, and a notepad or smartphone app to record results. Follow these steps: clean your hands, turn on the glucometer, prick your fingertip, apply blood to the test strip, stop bleeding, and record the results.

